Let’s Chop It Up!: Your Child’s Dental Health and Hygiene
Hey, mamas and daddies! If I had to pick one, I’d say dental hygiene is one of the most overlooked but impactful health practices. I mean it’s right up there with hand washing.
Here are a few things to consider when making choices regarding your babies’ dental health. Let’s go there!
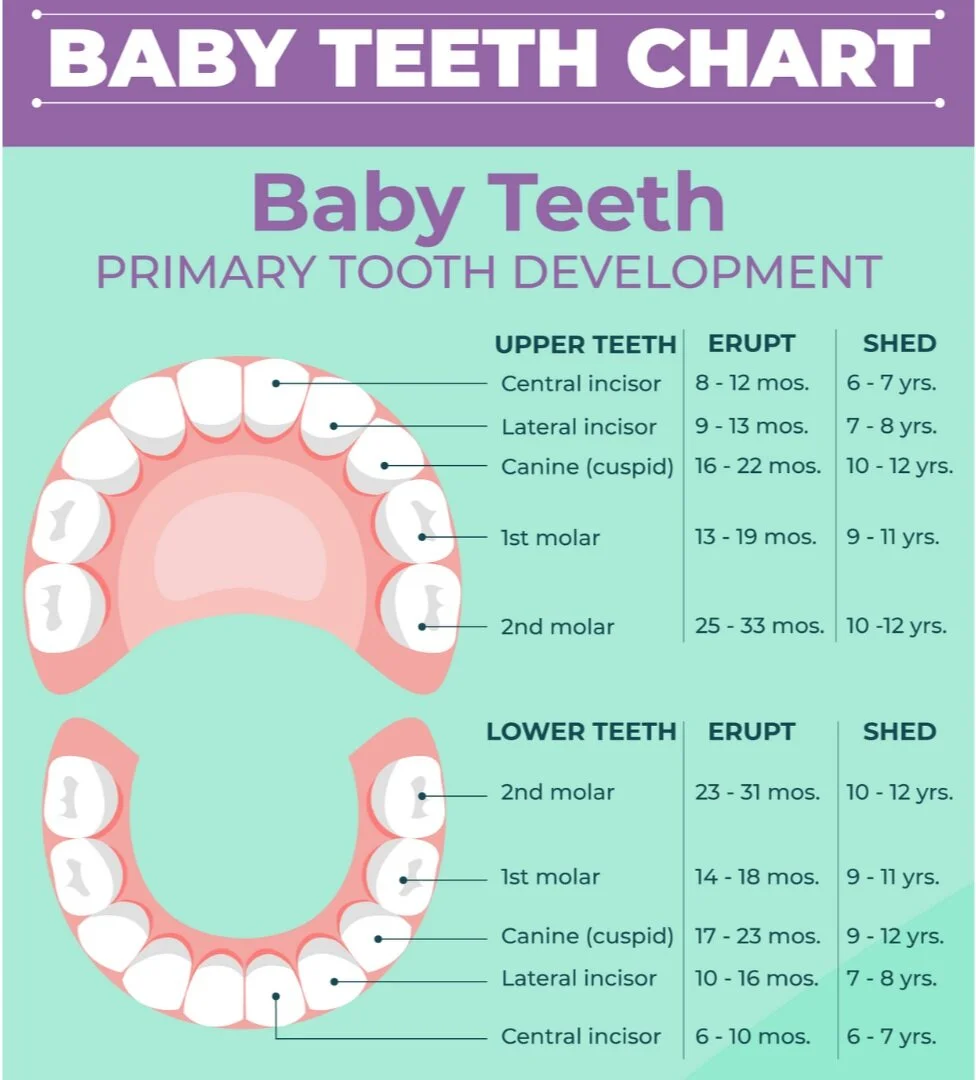
By the time our babies are born, their teeth have been developing since the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
They have 20 primary teeth growing and their teeth soon start “breaking” or “cutting” through the gums on average at 6-8 months old.
Infancy (Teething)
Before your baby starts teething, use a damp hand towel to clean their gums and tongue. This helps to clear away harmful bacteria and fungus that cause thrush.
Teeth can start erupting as early as 4 to 6 months.
Sign of teething include:
Irritability
Drooling/Skin Rashes
Biting and Gnawing
Low-Grade Fever
Cheek rubbing and ear pulling
Diarrhea
Clean chewing toys that have been chilled in the refrigerator are very soothing for their swollen and achy gums.
DO NOT USE numbing agents. They can affect your baby’s airway, and cause them to not be able to breathe.
When your baby’s teeth come in you can start brushing them with a soft infant toothbrush. Use water and a small amount of fluoride toothpaste (about the size of a grain of rice) that carries the American Dental Association's (ADA) seal of acceptance.
Schedule the first dental appointment on their first birthday, and ensure they see their dentist twice a year.
Pre-School
By age of 3, all 20 of your baby’s teeth have erupted.
Kids ages 3 and up should use only a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste. Be sure they spit out the toothpaste.
Your child may have already learned to spit while brushing their teeth. But still, help them brush until age 6.
The most common cause of tooth decay in young children is frequent, prolonged exposure of the teeth to sugar. So avoid sticky foods and snacks, candy, and sugary drinks.
Ask your dentist about when and how to floss your child’s teeth. The plastic flossing tools are helpful for parents to use for little children.
School-Age
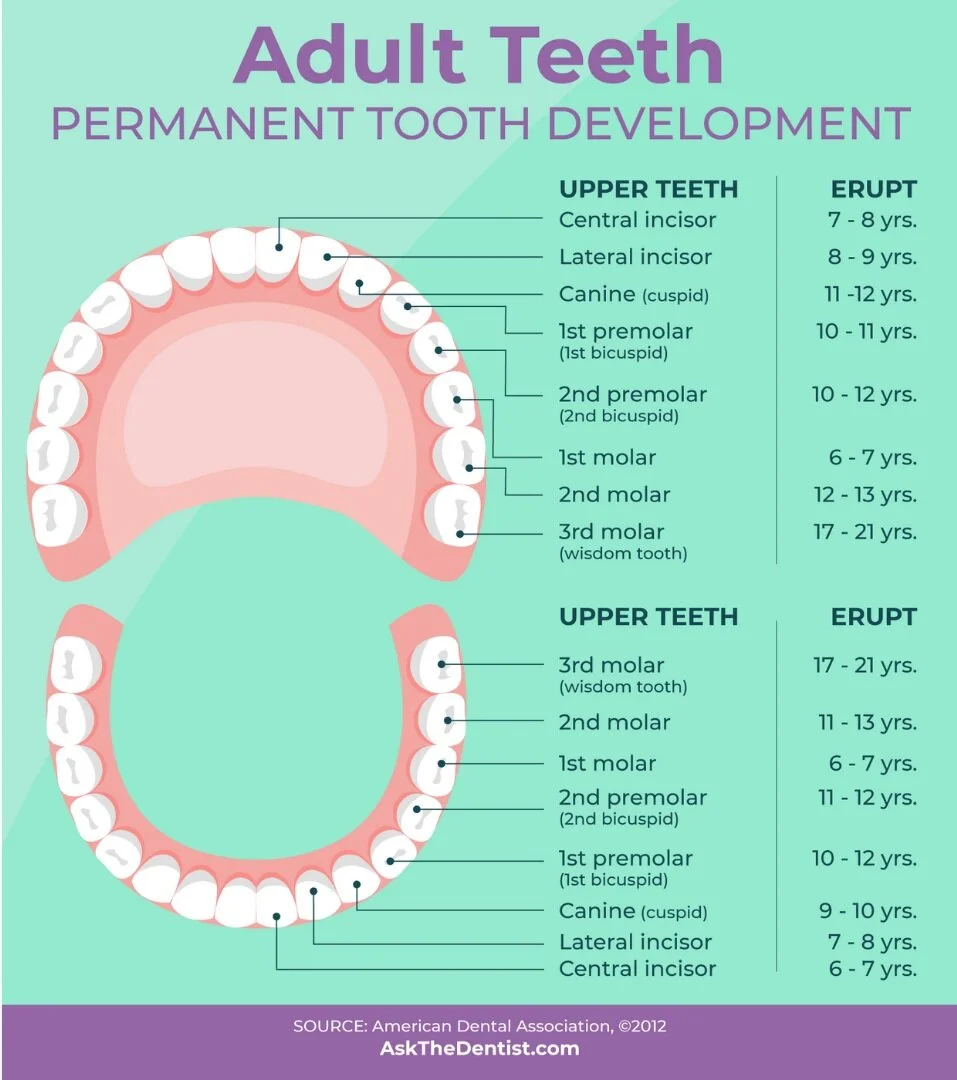
Your child may start losing teeth starting at age 5 to 6 years old, in preparation for their permanent tooth development.
The first permanent molars erupt at about age 6 behind the primary dentition of “baby teeth” without any baby teeth being lost.
These areas may be a little sore, and your children tend to not brush well back there because of the pain. So make sure to help them get back there and brush really well.
If you notice baby teeth that are lingering after the permanent tooth appears, that’s an indication to schedule an appointment with your child’s dentist.
If your school-aged children are at risk for having cavities because of sticky or sugary snacks or drinks, ask their dentist about applying fluoride varnish to prevent cavities.
Adolescents
If your child is wearing braces then you know they have a greater risk of developing cavities than children who don’t wear braces.
They need to brush and floss around their appliances more often, especially after eating.
Removable appliances should be removed to perform good oral hygiene and then re-inserted.
Ask your child’s dentist or orthodontist -the doctor that places braces on the teeth- about special toothbrushes and floss tools that help with ensuring optimal oral hygiene.
May this always be where all the children are well.
Parents, what questions do you have about your child’s dental health and hygiene? Comment below. I’d love you hear from you.
References
American Dental Association. 10 Things to Know About Your Tot's Teeth. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/babies-and-kids/kids-quick-tips?utm_source=mouthhealthyorg&utm_medium=mhkidsrotator&utm_content=toothcare
Ben-Joseph, E. (2018, June). Keeping Your Child's Teeth Healthy. KidsHealth. https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/healthy.html?WT.ac=ctg
Burhenne, M. (2020, June, 26). Baby Teeth: Eruption Charts, When They Fall Out, and Proper Care. https://askthedentist.com/baby-teeth/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, February, 4). Children's Oral Health. https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/basics/childrens-oral-health/index.html
Price, M.(2018, December, 13). Dental Care Through Their Ages, Part 2: Elementary School Children. Colgate Professional. https://www.colgateprofessional.com/dentist-resources/patient-care/dental-care-oral-health-elementary-school-children#